What Are Fault Codes?
Fault codes, or diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), are alphanumeric codes generated by the tractor’s onboard computer system when it detects a malfunction or irregularity. These codes are part of the tractor’s diagnostic system and provide specific information about the nature of the problem.
Where Do Fault Codes Appear?
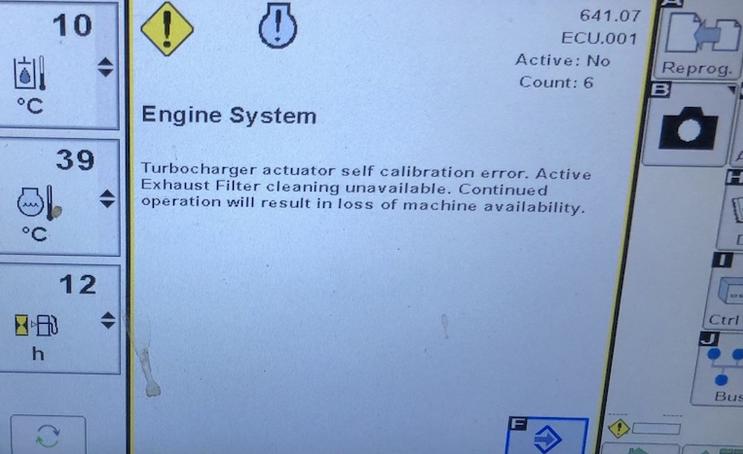
Fault codes typically appear on the tractor’s dashboard or control panel. They can also be accessed through a diagnostic tool connected to the tractor’s electronic control unit (ECU). When a fault occurs, the onboard computer logs the code and, in many cases, displays it on the screen for the operator to see. For example, The 5067E model offers a user-friendly approach to identifying trouble codes. When a sensor, such as the water in the fuel sensor, is disconnected or malfunctioning, it activates a warning light on the dashboard. To retrieve the specific code, press and hold the button on the steering column’s left side for approximately 5 seconds. This will cause the code, like ECU 9703, to appear on the display screen.
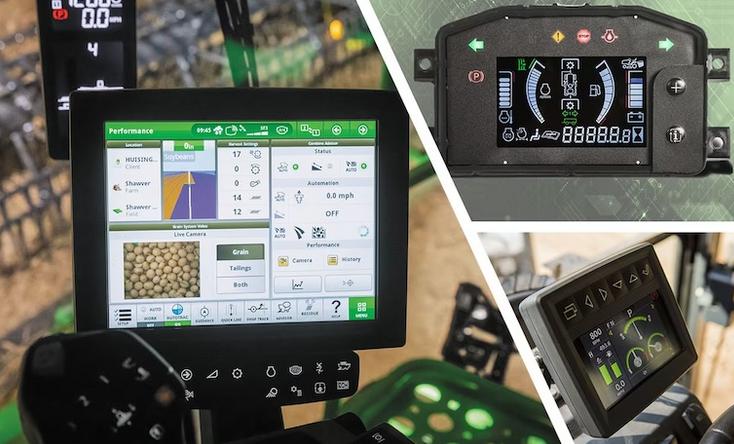

Tools Used to Diagnose Fault Codes
Diagnosing fault codes in John Deere tractors requires specific tools. The most common software is the John Deere Service Advisor, a comprehensive diagnostic and repair application designed for John Deere equipment. It allows technicians to access detailed information about the fault codes, perform tests, and update software.
Other tools include:
- Code Readers: Basic tools that read and display fault codes.
- Scan Tools: Advanced devices that provide more detailed information and troubleshooting steps.
- PC-Based Diagnostic Tools: Software installed on a computer that connects to the tractor’s ECU for in-depth diagnostics is a must-have hardware part of the JD Service Advisor.
Common Ways to Search for Fault Code Meanings
Finding the meaning of a fault code is crucial for troubleshooting. Here are some common methods:
- Owner’s Manual: The first place to check is the tractor’s owner’s manual, which often includes a list of common fault codes and their meanings.
- Online and Offline Databases: Websites provide comprehensive databases of fault codes and troubleshooting tips.
- John Deere Support: The official John Deere Service Advisor websiteis a dealer support resource that includes fault code lookup tools and service manuals.
- Community Forums: Online forums and communities, are valuable resources to find information shared by other tractor owners and experts.
Common John Deere Error Code Types
John Deere error codes can be categorized into several types based on the system they are related to. Here are some of the most common types:
- Engine Codes: Indicate issues related to the engine, such as overheating, low oil pressure, or fuel injection problems.
- Transmission Codes: These are related to the transmission system and include gear shifting issues or hydraulic problems.
- Hydraulic System Codes: These codes indicate problems with the hydraulic system, such as low hydraulic fluid levels or pump failures.
- Electrical System Codes: Pertains to the electrical system, including battery issues, wiring faults, or sensor failures.
- Auxiliary Codes: These codes relate to additional systems and accessories, such as PTO (Power Take-Off) or implement controls.
JD Error Codes abbreviation
These codes help identify issues in different tractor components, such as the engine, transmission, and other critical systems. Here is the list of John Deere error codes and explanation of their abbreviations
- ACU code– Armrest Controller Unit. These codes handle numerous functions, including hydraulics, transmission, and auxiliary system controls.
- AIC code– Armrest Integrated Controller Receives signals from the relevant operating controls
- ATC code– Controls the ClimaTrak automatic air conditioning system
- ASU code– Active Seat Control Unit
- BRC code– Front Brake Control Unit
- BCU code– Controls the basic functions of the tractor and the rear hitch
- BIF code– Basic Information – Controls the display, indicators, and instruments
- CAB code– CAB Control Unit
- CCU code– Chassis Control Unit, controls fuel level, iTEC™, alarms, differential lock, rear PTO, hydraulic, and air filter restriction
- CLC code– Cab Load Center Control Unit
- CRU code– Controls the functions of the radio
- CSC code– Controls the cab Suspension
- CSM code– Cabin Switch Module
- DSM code– Responsible for the keyboard of the DTI (quick access keys of the CommandCenter)
- DTI code– CommandCenter (DTI) – Allows the operator to carry out various adjustments and retrieve data
- ECU code– Controls the engine, managing fuel, air, and ignition systems
- EPC code– Controller for PowrQuad PLUS and AutoQuad transmissions
- ETC code– Controller for the heater and air conditioning system
- FCC code– Controls the wipers and processes signals from the turn-signal lever and reverse drive lever
- GPM code– Used for activation of the gear solenoids
- HCC code– Hitch Control Unit
- HTC code– Controller for the heater (no air conditioning system)
- HV1 code– Hitch Valve Control Unit
- ICC code– Instrument Cluster Control (tractor dashboard)
- JDL code– JDLink
- OIC code– Receives signals from the relevant operating controls
- PAP code– Controls the solenoids for PTO speed
- PDU code– Primary Display Unit (PDU)
- PLC code– Electronic Park Lock with AutoPowr/IVT Transmission
- PL1 code– Used for activation of park lock solenoid 1 (DirectDrive transmission)
- PL2 code– Used for activation of park lock solenoid 1 (DirectDrive transmission)
- PL3 code– Used for activation of park lock solenoid 2 (DirectDrive transmission)
- PL4 code– Used for activation of park lock solenoid 2 (DirectDrive transmission)
- PTA code– Controls the transmission on vehicles with AutoPowr™/IVT™ transmission
- PTD code– Used for activation of proportional solenoid valves for forward clutch and reverse brake
- PTF code– Controls the front PTO
- PTH code– Power Train Hydrostatic Control Unit
- PTI code– Power Train Control Unit
- PTP code– PowerShift Transmission Control Unit
- PTQ code– Controls the transmission on vehicles with PowrQuad™ transmission
- PTR code– Power Train Reverser
- RLC code– Controls the lights in the roof, the lights on the cab frame, the rear window heater, and the rear window wiper
- RPM code– Used for activation of the range of solenoids
- RPT code– Controls the rear PTO
- SCC code– Selective control valve CAN control unit
- SCO code– Controls the E-SCV selective control valves
- SFA code– Suspended Front Axle Control Unit
- SIC code– Control unit for the ESCVs/EICVs (Selective Control Valves)
- SSU code– Controller for AutoTrac automatic steering system
- SV1 code– Selective Control Valve Unit 1
- SV2 code– Selective Control Valve Unit 2
- SV3 code– Selective Control Valve Unit 3
- SV4 code– Selective Control Valve Unit 4
- SV5 code– Selective Control Valve Unit 5
- SV6 code– Selective Control Valve Unit 6
- SV7 code– Selective Control Valve Unit 7
- TCU code– Control unit for AutoPowr/IVT transmission
- TEC code– Interface for tractor equipment (ISOBUS)
- TEI code– Tractor Electronic Interface
- TIA code– Controls the transmission on vehicles with AutoPowr™/IVT™ transmission
- TID code– Activation of the transmission enable function
- TIQ code– Transmits signals to the PTQ control software
- TSC code– Controls, coordinates, and manages all functions required for front wheel drive axle and cab suspension
- UIC code– Transmission Control with AutoPowr/IVT Transmission
- UIM code– User Interface Module, responsible for the keyboard of the GreenStar Display 2100/2400
- VLC code– Vehicle Load Center (VLC) Control Unit
- VTV code– Controls the CommandCenter™ display
- VTI code– Controls the GreenStar Display 2100/2600
- XMC code– Controls the AutoTrac™ automatic steering system
- XSC code– Controls the AutoTrac™ automatic steering system
We will enrich the list of JD error codes with particular error codes and their explanations. So stay tuned
Conclusion
Understanding and diagnosing fault codes in John Deere tractors is essential for maintaining their performance and reliability. You can quickly identify and resolve issues using the right tools and resources, ensuring your tractor remains in optimal working condition. Whether you’re a seasoned operator or a new owner, being familiar with fault codes and their meanings is an invaluable skill.
