Vehicle Speed Sensor
The Vehicle Speed Sensor, or VSS, generates electrical pulses that are sent to the vehicle’s onboard engine computer, commonly known as the PCM or ECU, through a magnet that spins a sensor coil. The frequency of the pulse rises as the vehicle’s speed increases. These sensors are typically installed in the vehicle’s transmission, differential, or near the wheels to properly monitor vehicle speed.
3 Common Types Of Vehicle Speed Sensors
1.) Speed Sensors Based On The Hall Effect
The ignition key provides +12V to the VSS. The Hall switch is turned on and off in sequence as the tachometer speed cable rotates, sending a rectangle signal to the onboard computer. The car’s speed is determined by the frequency of this signal.
2.) Speed Sensors With Mechanical Tenon
The signal generated by the rotating driving wheel is rectangular in shape. The signal voltage ranges from 0V to +5 V, or from 0V to a value similar to the automobile battery’s normal voltage. The duty cycle for pulses varies between 40% and 60%.
3.) Inductive Speed Sensors
The signal generated by the rotating driving wheel is sinusoidal (alternative current). As with any inductive sensor, such as the ABS sensor, the signal changes based on the speed of the wheels.
5 Symptoms of a Faulty Speed Sensor
1.) Issues With Transmission
The transmission control module (TCM) or powertrain control module (PCM) uses the vehicle speed information received by the VSS to determine shift time. As a result, if a speed sensor fails, it will have a direct impact on automatic gearbox operation. Abnormal automatic transmission operation is one of the most prevalent indicators of a defective speed sensor. The transmission may exhibit symptoms such as delayed shifts, harsh shifts, and limited gear performance if the VSS is faulty.
2.) Speedometer Readings That Are Erroneous
Because the VSS is a main input for many vehicles’ speedometers, a faulty VSS can cause the speedometer to provide irregular readings—or no readings at all. Your vehicle will continue to run even if the speedometer is broken. However, driving safely will be tough if you don’t know how fast you’re travelling.
3.) The Inability To Use Cruise Control
When the PCM fails to receive information from the VSS, the cruise control in your car is often deactivated. This is due to the fact that the system requires sensor data in order to maintain your automobile operating at a steady pace.
4.) Application Of Torque Converter Clutches Is Lacking.
The torque converter clutch is engaged at a predetermined speed. The transmission torque converter will be unable to engage the clutch and make a mechanical relationship between the engine and gearbox without precise information from the vehicle speed sensors. This can result in sliding, decreased fuel efficiency, and an overheated gearbox.
5.) The Check Engine Light Has Illuminated.
The PCM can cause your vehicle’s check engine light to illuminate for a variety of reasons, one of which is a defective VSS. To determine whether the error code indicates a VSS problem, connect your car to an OBD-II scan tool. Other warning lights on the dashboard, such as those for the ABS and traction control systems, may also display.
Can You Drive With A Faulty Vehicle Speed Sensor?
In general, driving a vehicle with a broken wheel speed sensor is dangerous. Because the car’s computer cannot identify the speed at which your vehicle is driving, it may apply the brakes more quickly than necessary or increase engine power.
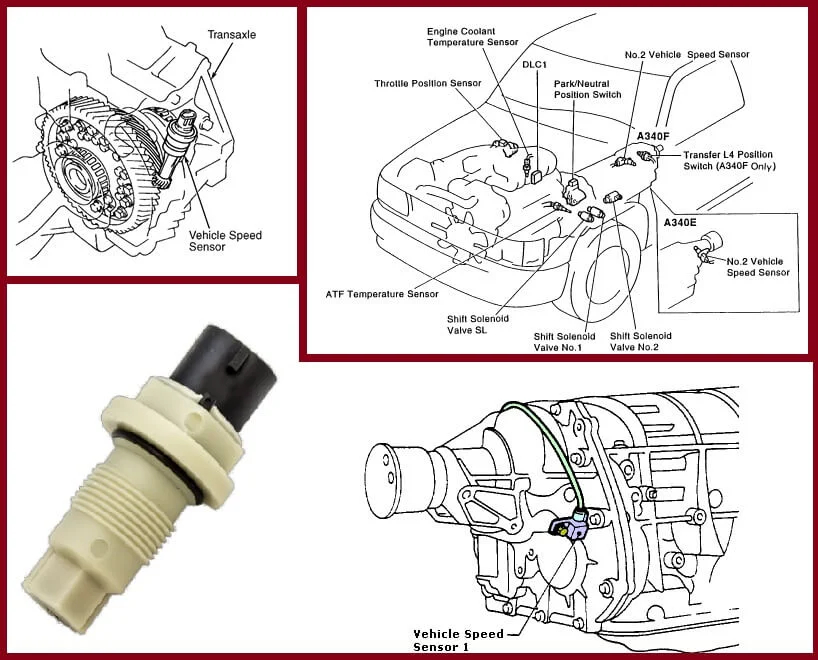
The Most Common Location Of Your Car’s Vehicle Speed Sensor
A vehicle speed sensor is often installed on the side of a wheel axle or traction motor axle and driven by a pin pushed into the axle.
4 OBD DTC Related to Vehicle Speed Sensor
* P0503 Vehicle Speed Sensor Intermittent/erratic/high
* p0502 Vehicle Speed Sensor Low Input
* p0501 Vehicle Speed Sensor Range/performance
* p0500 Vehicle Speed Sensor Malfunction
The following are the most prevalent reasons why DTC is detected.
* Excessive metal debris accumulation on the speed sensor/s
* A faulty wheel speed sensor or vehicle speed sensor
* Wiring harnesses or connectors that have been cut or otherwise damaged (especially near speed sensors)
* Teeth on a reluctor ring that have been damaged or worn
* A PCM, ABCM, or EBCM that is malfunctioning